Innovation in the production of ethyl acetate, acetic aldehyde, and acetic acid has been driven by the need for more sustainable and efficient processes, as well as the increasing demand for these chemicals in various industries. Let's explore some of the recent innovations in their production.
1. Ethyl Acetate:
Ethyl acetate is a widely used solvent in industries such as paints, coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals. Innovations in its production have focused on improving process efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Some notable advancements include:
a. Bio-based Ethyl Acetate:
Researchers have been exploring the use of renewable feedstocks to produce ethyl acetate, moving away from fossil fuel-based resources. One approach involves utilizing lignocellulosic biomass, such as agricultural waste or dedicated energy crops, as a feedstock. By employing enzymatic or microbial processes, the biomass can be converted into sugars, which are then fermented to produce ethyl acetate. This bio-based approach offers a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional petrochemical-based production methods.
b. Catalytic Innovations:
Catalytic innovations have focused on developing more efficient and selective catalysts for the production of ethyl acetate. For example, researchers have explored the use of solid acid catalysts, such as zeolites or modified metal oxides, which offer improved conversion rates and selectivity. These catalysts can enhance the reaction efficiency and reduce the energy requirements of the process.
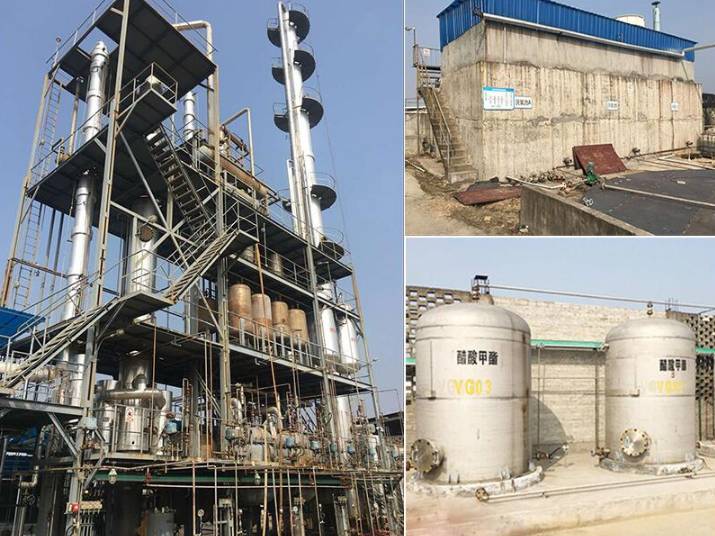

2. Acetic Aldehyde (Acetaldehyde):
Acetic aldehyde is a key intermediate chemical used in the production of various downstream products, including acetic acid, ethyl acetate, and plastics. Innovations in its production have aimed at improving process efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing environmental impact. Some notable advancements include:
a. Bio-based Acetic Aldehyde:
Similar to ethyl acetate, the production of bio-based acetic aldehyde has gained attention. Renewable feedstocks, such as glucose or other sugars derived from biomass, can be utilized as a starting material. Microorganisms or enzymatic processes can convert the sugars into acetic aldehyde through fermentation or bioconversion routes. This approach offers a more sustainable and renewable source of acetic aldehyde, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
b. Advanced Oxidation Technologies:
Traditional methods for acetic aldehyde production involve the oxidation of ethanol. Recent innovations have focused on developing advanced oxidation technologies to improve process efficiency and selectivity. For example, researchers have explored the use of novel catalysts, such as metal oxides or supported noble metal catalysts, to enhance the oxidation reaction. These catalysts can provide higher conversion rates, selectivity, and improved energy efficiency.
3. Acetic Acid:
Acetic acid is a versatile chemical widely used in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and plastics. Innovations in its production have focused on reducing energy consumption, improving process economics, and minimizing environmental impact. Some notable advancements include:
a. Methanol Carbonylation:
One significant innovation in acetic acid production is the methanol carbonylation process. This process involves the reaction of methanol with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst to produce acetic acid. Advancements in catalyst technology, such as rhodium-based catalysts, have improved the reaction efficiency, selectivity, and overall process economics. Methanol carbonylation offers a more sustainable and energy-efficient alternative to traditional acetic acid production methods.
b. Bio-based Acetic Acid:
Bio-based acetic acid production has gained attention as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-based methods. It involves the fermentation of renewable feedstocks, such as sugars derived from biomass or agricultural waste, by microbial processes. The fermentation route produces ethanol, which is subsequently oxidized to acetic acid. This bio-based approach offers a reduced carbon footprint and decreased dependence on non-renewable resources.
Conclusion
Innovation in the production of ethyl acetate, acetic aldehyde, and acetic acid has focused on sustainability, process efficiency, and environmental impact reduction. Bio-based routes utilizing renewable feedstocks, advanced catalytic technologies, and improved oxidation processes have played a significant role in driving these innovations. As the demand for these chemicals continues to grow, ongoing research and development efforts will likely lead to further improvements in their production methods.
Please contact us for professional help if you need it.