Phenol Alkylation Plant
The alkylation reaction of phenol refers to the reaction process in which hydrogen atoms in phenol are substituted and alkyl groups are introduced. There are many methods available for this reaction, and different methods can be chosen depending on the reaction conditions, substrates and catalysts.
1.Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction:
Friedel-crafs alkylation reaction is a commonly used method for the alkylation of phenol. It was proposed by Charles Friedel and James Krafts in the 19th century and was one of the first alkylation methods discovered. Mainly achieved through acid catalysis.
The specific mechanism of the reaction is: first, the acid catalyst (such as aluminum chloride, sulfuric acid or thionyl chloride) is complexed with Brönsted or Lewis acid to generate active ions; then, phenol interacts with the active ions through the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom. A complex is generated; finally, the alkyl ions in the complex undergo nucleophilic substitution to form the target product.
2. Direct alkylation reaction:
Direct alkylation is a method that does not require the use of an acid catalyst and is carried out under high temperature or high pressure conditions. This method mainly utilizes free radical substitution reactions during the alkylation of phenol.
The specific mechanism of the reaction is: at high temperature, the alkyl halide or organic halide in the solvent or steam decomposes to generate free radicals, and then undergoes a free radical substitution reaction with phenol to generate the corresponding alkyl phenyl alcohol product. This method has the advantages of simple operation and mild reaction conditions. 3. Alkylation reaction using alkali catalyst:
Alkylation using a base catalyst is a method of selective alkylation. In this method, selective alkylation is achieved by protonation of the phenol and neutralization of the functional groups in the base. The most commonly used bases are alkali metals (such as sodium or potassium), basic metal hydrocarbonates (such as sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate), etc.
The specific mechanism of the reaction is: first, phenol generates a protonated product through a protonation reaction; then the protonated product is neutralized with the functional group in the base to generate the corresponding product. This method is suitable for alkylation reactions with higher reactive alkylating reagents and will produce fewer side reactions and by-products because a base catalyst is used instead of an acid catalyst.
The above are some common alkylation reaction methods of phenol. Different methods are suitable for different practical application needs. These methods can be selected according to different reaction conditions, substrates and catalysts to achieve alkylation substitution of phenol and obtain the desired target product g
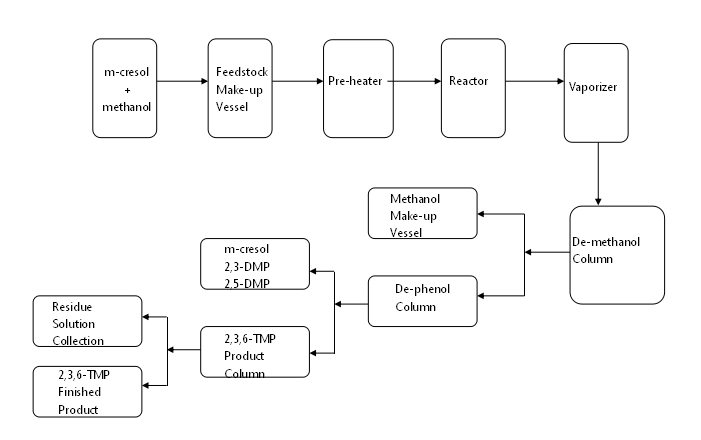
Alkyl phenol is produced by the alkylation of phenol by reacting with olefin, aliphatic alcohol, or chloro-hydrocarbon. They are important intermediates for fine chemical synthesis, widely applied in the manufacture of surface active agent, anti-oxidation agent, paint and coating. SL TEC offers the technology of phenol’s alkylation into o-cresol, and cresol’s alkylation into 2-t-butyl-p-cresol, 6-t-butyl-m-cresol, 2,6-di-t-butyl-p-cresol, 2,3,6-trimethylphenol (2,3,6-TMP) and etc.
Also SL TEC supplies the technology of producing m-cresol/p-cresol by the isomerization of o-cresol.